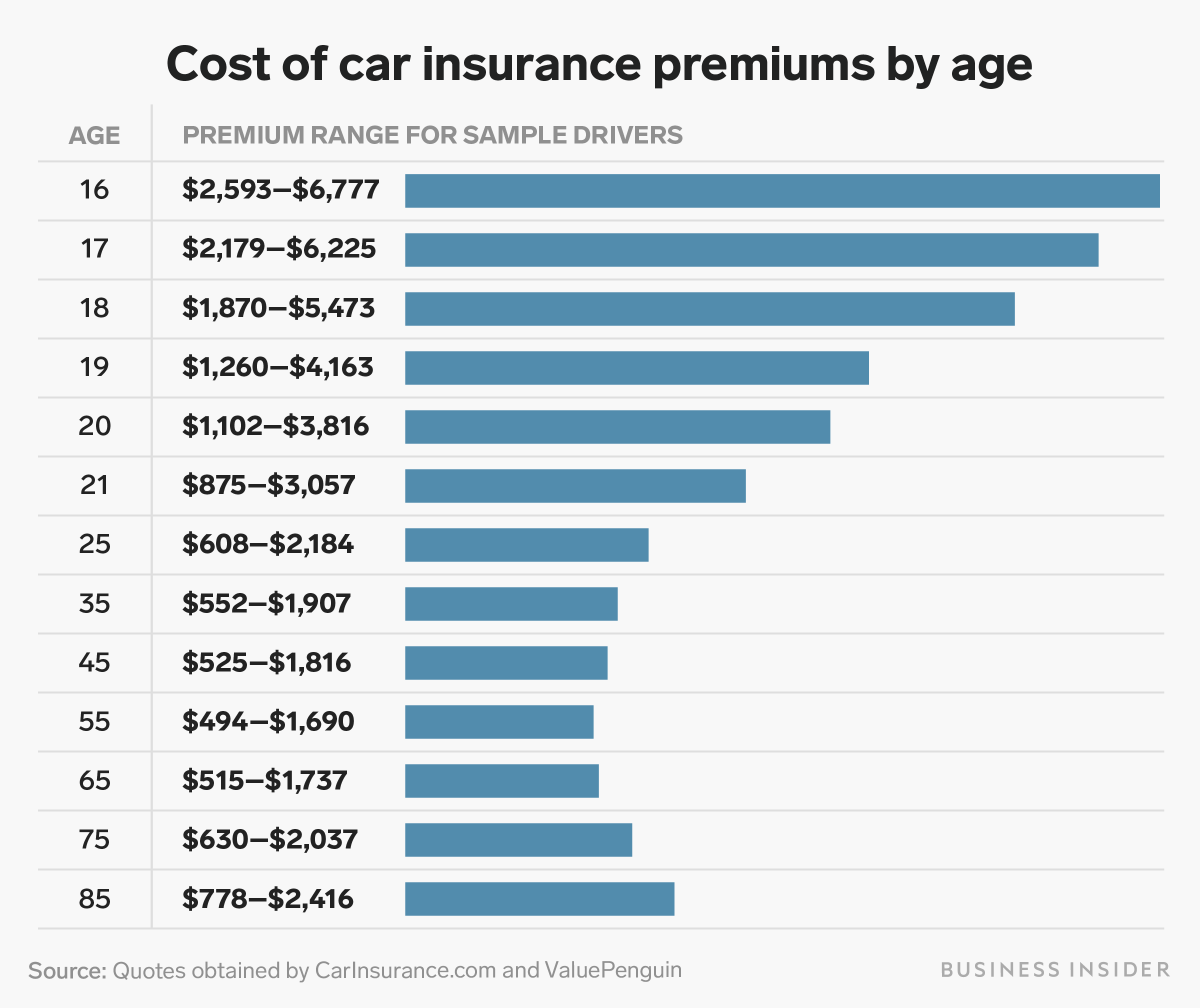2023 outlook for car insurance buyers: Here’s the bill
Editor’s note: We earn a commission from affiliate links on Forbes Advisor. Commissions do not influence the opinions or ratings of our editors.
Inflation, continued supply chain issues, and costly car accidents will lead the way to higher car insurance costs in 2023.
During the height of the pandemic, with driving greatly reduced, accidents and claims also decreased. Now drivers are back on the road, and the resulting accidents cost a lot more in auto insurance claims thanks to more expensive parts, labor and medical bills.
The rising cost of car insurance is the main trend car insurance buyers can expect to see in 2023, and here are the main contributing factors.
Inflation Catapults Car Insurance Costs Higher
Contents
- 1 Inflation Catapults Car Insurance Costs Higher
- 2 Severe Car Crashes Lead to Costly Medical Claims
- 3 Auto Repair Costs Continue to Soar
- 4 Lawsuits Lead to Large Payouts and Then Rate Hikes
- 5 Best Car Insurance Companies 2022
- 6 Is it better to pay house insurance monthly or annually?
- 7 What has the biggest impact on your vehicle insurance premium?
- 8 How much is the car insurance industry worth annually?
- 9 Do home insurance premiums ever go down?
The Consumer Price Index (CPI) saw an increase of 7.7% for the 12-month period ending in October 2022. This may interest you : GEICO can pay $ 5.2 million for an STD woman in an insurance car. The CPI saw its biggest 12-month increase in 40 years, in June 2022, when the CPI rose 9.1%.
The cost of food, housing, energy and other everyday items – including car insurance – are evaluated for the CPI, which helps measure inflation and track its rate of change over time.
The cost of car insurance rose by 1.7% from September to October 2022, the seventh straight month in a row. And year-over-year car insurance prices are up a whopping 12.9%, according to CPI data. Compared to September 2020, car insurance costs have increased by an incredible 19.9%.
A new report from the American Property Casualty Insurance Association (APCIA), a trade group for property/casualty insurers, examined the struggle of auto insurance companies with inflation. The APCIA says that insurance claim costs are rising faster than the CPI and the increase in car insurance companies’ rates. As auto insurance companies feel behind, expect to see more rate increases in 2023 as they try to catch up.
“One of the big concerns facing consumers for 2023 is the relentless pace of auto insurance rate increases,” says Douglas Heller, director of insurance at the Consumer Federation of America.
Auto insurance company rate increases have already been approved or filed with state regulatory departments, but they’re just starting to roll in. Heller expects drivers to see significant rate increases when they come to politicians for renewals — or they buy new auto insurance — over the next six to nine months.
Severe Car Crashes Lead to Costly Medical Claims
People are back on the road and driving more than ever. Data from the Federal Highway Administration shows 43. See the article : DC car thefts, inflation driving up car insurance rates.2 billion miles traveled by vehicles in the first half of 2022, an increase of 2.8% compared to the same period in 2021.
More kilometers driven, drivers have more chances to crash. Estimates from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) for the first quarter (January to March) of 2022 show 9,560 car crashes, the highest number of fatalities in the first quarter of a year since 2002. That’s a 7% increase in deaths compared to 2021.
The APCIA points out in its report that the frequency of injury claims has decreased by almost 25% in recent years, but the severity of injuries has increased by almost 40%. That makes the insurance payouts for injury claims higher, and this will ultimately increase to all drivers in the form of car insurance rates.
The average cost per collision claim (known as collision claim severity) reached $5,743 in the first quarter of 2022, according to the APCIA. That’s a new record high and 36.5% higher than the first quarter of 2020. Meanwhile, auto insurance companies increased auto insurance rates by just 4.6%.
There is a glimmer of hope that a reversal of the auto accident fatality trend is coming. NHTSA estimates for the second quarter of 2022 (April to June) show a 4.9% decrease in fatal car crashes compared to 2021. When the number of serious crashes begins to decline, there is a chance for to reduce future car insurance increases – but they are still on their way.
Auto Repair Costs Continue to Soar
Car accidents also come with damage claims for the burned vehicles. Inflation has also hit this area hard, with high costs for parts and labor. On the same subject : Why your car insurance could keep you away from urgent care : Shots – Health News. Further supply chain issues make aftermarket and OEM (original equipment manufacturer) parts difficult to find and cause a serious backlog at repair shops, which only adds to the cost of car insurance claims.
A report by Enterprise Rent-a-Car tracked how long rental cars were used by drivers waiting for their cars to be repaired after accidents. Enterprise found that the average time car owners waited for collision repair was 18.2 days for the second quarter of 2022, up 4.5 days from last year.
Repair times have grown significantly, resulting in additional pressure for insurance companies to raise auto insurance rates, says Rich Attanasio, senior director at AM Best, a credit rating agency and data analytics provider specializing in the insurance industry.
“Many personal auto insurers continue to pursue rate increases in response to worsening claims costs driven by several factors: the higher rate of fatalities, increases in the cost of repairing newer vehicles, higher used car prices, supply chain and labor market challenges and rising medical costs “, says Attanasio.
Mark Friedlander, director of corporate communications at the Insurance Information Institute, agrees: “Personal auto insurance premiums have remained relatively flat this year, despite significant increases in the consumer price index (CPI), vehicle prices, and the cost of auto parts.”
Other factors that Friedlander notes are putting pressure on auto insurance companies to raise rates include higher used car values, higher auto repair costs, and increased comprehensive claims from catalytic converter theft.
Lawsuits Lead to Large Payouts and Then Rate Hikes
A major concern heading into 2023 for auto insurance companies is excess claim payouts due to lawsuits. A study by the Insurance Research Council found that lawyers involved in auto insurance claims involving injuries are associated with higher claim costs and settlement delays.
The APCIA report finds that litigation claims are increasing at previously unseen rates. This includes increases in verdicts and some with exceptionally high jury awards, including billion-dollar personal injury verdicts. The concern for auto insurance companies is that these major laws will set new precedents that will bring about “close inflation.”
The Insurance Information Institute has a brief on social inflation and its effects on auto insurance companies. It explains how social inflation relates to the impact of rising litigation costs on insurance companies’ payouts, their loss ratios (how much an insurance company pays out for claims compared to how much they receive in premiums) and ultimately how much we as Insurance pay car insurance.
A research paper by the Insurance Information Institute and the Casualty Actuarial Society found between 2010 and 2019, social inflation increased commercial auto liability claims by over $20 billion. There is evidence that similar trends are happening in other lines, with insurance companies fearing that it will be in personal car insurance.
High court and judgment costs involving car insurance companies are passed on to drivers in the form of higher car insurance costs.
All in all, the bill came due to multiple costs, and car insurance companies always try to pass the costs on to customers.
Best Car Insurance Companies 2022
With so many choices for car insurance companies, it can be difficult to know where to start to find the right car insurance. We’ve rated insurers to find the best car insurance companies so you don’t have to.
Is it better to pay house insurance monthly or annually?
Paying annually can help you save in the long run, but it’s not the best option for everyone. If you haven’t built up the savings to withstand a big withdrawal, get more practical with monthly payments. If you have the resources, paying annually can bring you some nice savings every year.
Is it better to pay for homeowners insurance through escrow? Escrow accounts can provide peace of mind and convenience as they reduce the burden of paying your homeowner’s insurance premiums and property taxes yourself. Another advantage is that you can still shop around with different insurers if you want and save money by changing your policy.
Is it cheaper to pay insurance yearly?
Paying your insurance premiums annually is almost always the least expensive option. Many companies will give you a discount for paying in full because it costs more for the insurance company if a policyholder pays their premiums every month because that requires manual processing every month to keep the policy active.
Is it cheaper to pay insurance all at once?
In 2021, drivers who paid full premiums saved about 4.7% on average, according to Zebra, an insurance comparison website. And saving money isn’t the only potential benefit of paying up front. With the premium payment out of the way, you have one less monthly bill to worry about.
For most people, monthly payments are best because they are easier to factor into your budget. But if you can afford to pay a lump sum each year, you may be eligible for an annual premium discount of up to 5%, depending on your policy and insurer.
Is insurance cheaper if you pay yearly?
Benefits of Paying Homeowners Insurance Annually You usually get a lower rate than you would if you paid it monthly. Even if your mortgage lender allows you to make monthly payments, if you are allowed to pay the premium immediately, the savings can be significant.
What is a good monthly payment for home insurance?
In the United States as a whole, the average cost of homeowners insurance is $1,680 per year and $140 per month – but the cost of coverage varies significantly based on state laws, your home location and the cost of rebuilding.
Is it better to pay home insurance in full or monthly?
Benefits of Paying Homeowners Insurance Annually You usually get a lower rate than you would if you paid it monthly. Even if your mortgage lender allows you to make monthly payments, if you are allowed to pay the premium immediately, the savings can be significant.
Why is homeowners insurance so expensive?
On average, the most expensive states for homeowner insurance in 2022 are Oklahoma, Nebraska, and Kansas, while the least expensive states are Hawaii, Utah, and Vermont. Homeowners insurance costs are rising, likely due to inflation, supply chain disruptions and increased costs for materials and labor.
Who has the most reasonable home insurance?
Our cheapest homeowners insurance companies of 2022
- #1 State Farm.
- #2 Nationwide.
- #3 Farming.
- #4 American family. #5 Friend.
Is it better to pay yearly or monthly?
If the interest rate is less than what you would pay on a credit card or other loan to pay off the balance in advance, then it makes sense to use the monthly method. If the rate is more than you pay from other financing, then you should borrow from this alternative financing source and make a single annual payment.
What’s the difference between monthly and annually?
The monthly billing plan charges your payment method on the first day of each month. The annual billing plan is charged once a year on the date the plan was started and offers a free monthly subscription compared to the monthly plan.
Is it better to pay car insurance monthly or every 6 months?
“Paying your car insurance premium every six months will save you money. Depending on the insurance company, this can significantly reduce your premium compared to monthly payments.
What bills can you pay yearly?
Which bills should you pay annually instead of monthly?
- RichVintage/Getty Images. Many people pay their bills every month. …
- Car insurance. …
- Property taxes. …
- Tuition payment. …
- Homeowners insurance. …
- Gym membership. …
- Subscription Services. …
- Life insurance.
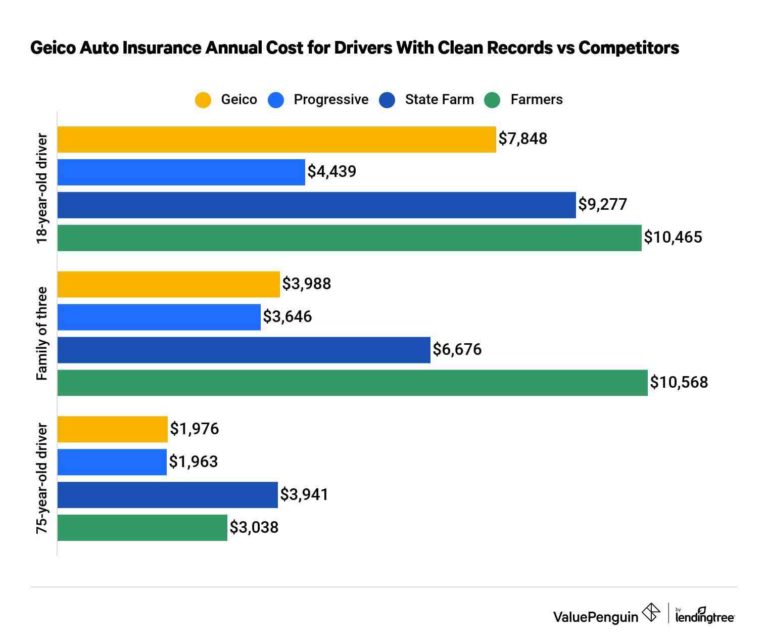
The biggest factors that affect car insurance rates are state coverage requirements, age, and the make and model of the car. The more coverage you need to purchase in your state and the more valuable your vehicle is, the more you will pay for auto insurance.
Which factor affects insurance premiums the most? What factors are most important for car insurance rates?
- Age. Age is a very significant rating factor, especially for young drivers. …
- Driving history. This rating factor is simple. …
- Credit score. …
- Years of driving experience. …
- Location. …
- Gender. …
- Insurance history. …
- Annual mileage.
Car accidents and traffic violations are common explanations for an insurance rate increase, but there are other reasons why car insurance premiums increase, including a change of address, new vehicle and claims in your zip code.
Five factors can affect a plan’s monthly price: location, age, tobacco use, plan category, and whether the plan covers dependents. Note: FYI your health, medical history or gender cannot affect your premium.
How much is the car insurance industry worth annually?
1. The US auto insurance industry is worth $288.4 billion.
How much money does the auto insurance industry make? Recent estimates put the size of the US auto insurance industry at more than $280 billion per year and growing at a healthy 2.7% annual average over the past five years.
How big is the car insurance market?
| Market | Vehicle insurance market |
|---|---|
| Base year | 2021 |
| forecast data | 2022 – 2030 |
How much is the insurance industry worth 2022?
The global insurance market is expected to grow from $5,376.92 billion in 2021 to $5,938.41 billion in 2022 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4%. The market is expected to grow to $8,398.11 billion in 2026 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1%.
How much is the car insurance industry worth?
The market size, measured by revenue, of the automobile insurance industry will be $316.2bn in 2022. What will be the growth rate of the automobile insurance industry in the United States in 2022? The market size of the car insurance industry is expected to increase by 1.7% in 2022.
What is the insurance industry worth?
Insurance is one of the largest industries in the world, with a global market value greater than the gross domestic product (GDP) of many countries. While estimates may vary, most sources put the figure at around 5.5 trillion US dollars of insurance premiums written in 2021.
How much is the car insurance industry worth UK?
The UK car insurance industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.3% from GBP18. 4 billion ($25.5 billion) in 2021 to 20 GBP. 6 billion ($31.3 billion) in 2026, in terms of direct written premiums (DWP), according to GlobalData, a leading data and analysis company.
How much is the car insurance industry worth UK?
The UK car insurance industry is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 2.3% from GBP18. 4 billion ($25.5 billion) in 2021 to 20 GBP. 6 billion ($31.3 billion) in 2026, in terms of direct written premiums (DWP), according to GlobalData, a leading data and analysis company.
How much is the insurance industry worth 2022?
The global insurance market is expected to grow from $5,376.92 billion in 2021 to $5,938.41 billion in 2022 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.4%. The market is expected to grow to $8,398.11 billion in 2026 at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.1%.
Hartwig, president of the Insurance Information Institute. Even if your home is worth less now than it was a few years ago, chances are you will pay the same amount for your insurance premiums, maybe even more. While the price of houses may decrease in some areas, the cost of labor and materials is not.
.